Piping Systems
Compressed air system with network planning
Design the most efficient compressed air system with the expertise of TOPRING and assistance from AIR COMPPOWER.
“Begin by considering the unique requirements of your compressed air system project, taking into account the specific application, equipment, usage frequency, layout and working environment conditions to ensure safety, efficiency, and performance.”
Compressed air system configuration
“Air networks provide an efficient means of distributing compressed air to various locations within a building. Depending on the chosen piping material, these networks bring several benefits, including modularity, swift installation, robustness, and the added advantages of lower maintenance and operating expenses.
The optimal configuration of a compressed air network is determined according to the layout of the plant or workshop. The goal is to achieve a balance between the demand in air volume, i.e. the flow rate measured in SCFM, and the pressure required in PSI. It’s also important to think about and plan for your future needs, such as expansion projects. This step will allow you to determine the right diameter of the main network not just for your current requirements but also for the future.
The two most common configurations:
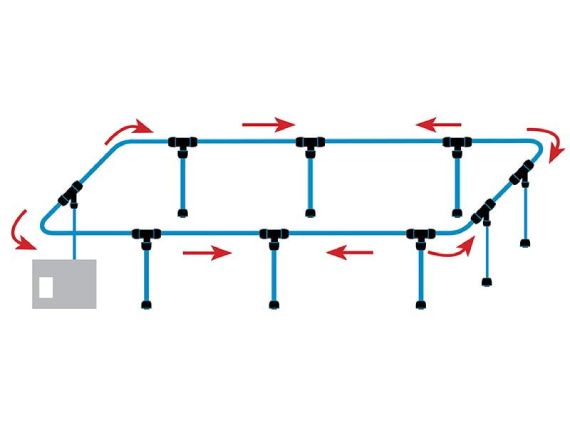
Closed-loop system
Closed-loop systems are considered the most efficient configuration. They promote uniform pressure between all compressed air sampling points. Prioritize this type of configuration if your layout allows it.
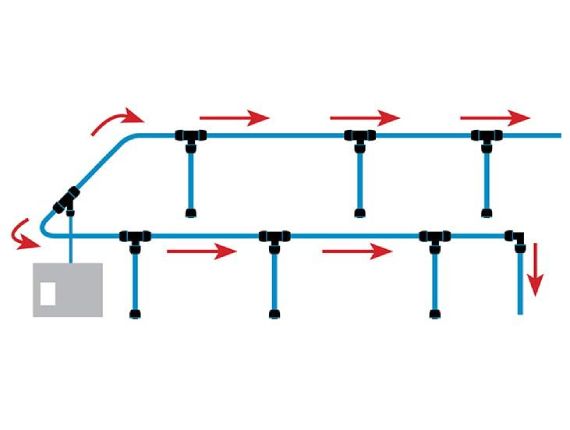
Linear system
Opt for a linear network when a closed-loop configuration is not possible. To feed the network in both directions, the compressor should ideally be located in the center of the network (from the compressor to the furthest point of use) or you could have more than one compressor.
The ISO Standard
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established the 8573 air quality standard to assist in the selection, design, and measurement of air handling components. Refer to this standard to see what requirements apply to your industry.

Compressed air without specification
ISO 8573.1 Class 5.6.5

General shop air: Air tools (sand blasting, grinding)
ISO 8573.1 Class 3.6.4

Air instrument Spray painting Powder coating Packing machines
ISO 8573.1 Class 1.5.3

Food industry Pharmaceutical and chemical industries Laboratories
ISO 8573.1 Class 1.4.1

Food industry (breweries, dairies) Pharmaceutical and chemical industries Laboratories
ISO 8573.1 Class 1.1.1
To know more feel free to contact us: info@aircomppower.com

